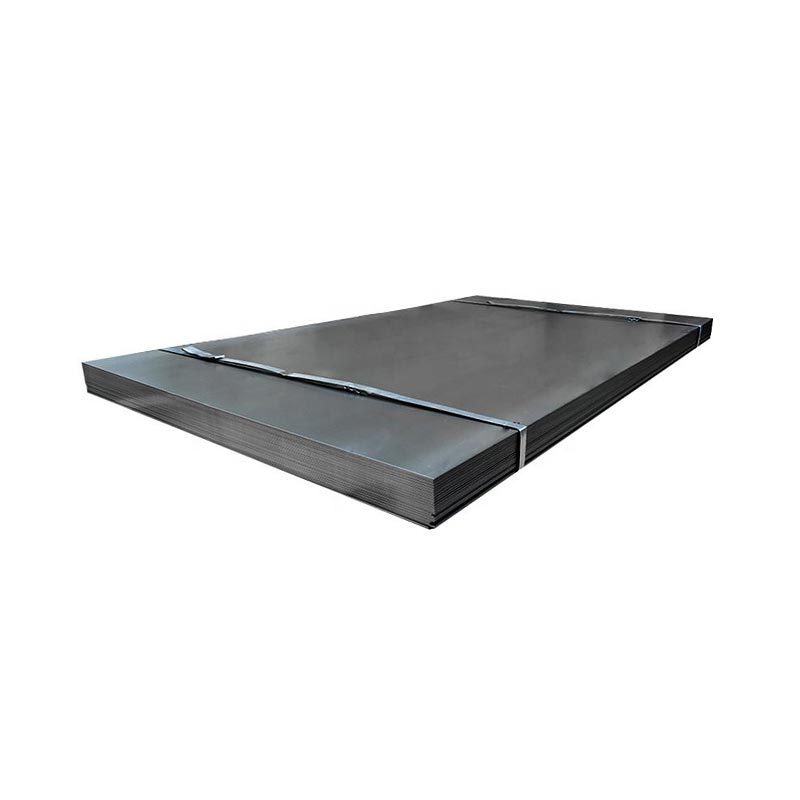
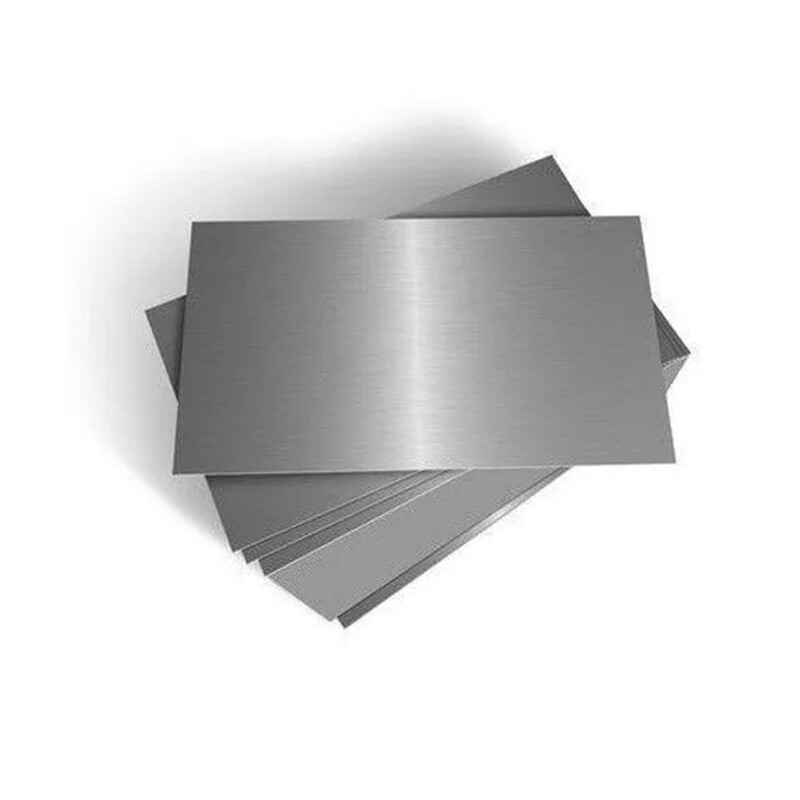
Carbon Steel Plate
● A carbon steel plate is a flat sheet made from carbon steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, with minimal other elements. It’s categorized by carbon content: low (≤0.25%), medium (0.25–0.6%), and high (>0.6%).
● Low-carbon plates offer ductility and weldability, ideal for construction or automotive parts. Medium-carbon variants balance strength and toughness, used in machinery. High-carbon types are hard but brittle, suited for tools or springs.
● Common grades include A36, S235JR, and A572. These plates vary in thickness, width, and finish, serving industries like construction, manufacturing, and energy for structural, industrial, or fabrication needs.
View Video
Manganese Plate
Manganese plates are steel plates with varying manganese content, tailored for strength and durability. Low-manganese types (0.5%-1.0% Mn) suit general structures. Medium grades (1.0%-1.5% Mn) offer higher strength for gears/shafts. High-manganese plates (11%-14% Mn) excel in wear resistance and toughness, ideal for mining/crushing equipment. They enhance steel’s hardness and impact resistance, used across machinery, automotive, and heavy industries.
Get A Quick Quote!
You Can Leave Us A Message
or Send Us An Email!
Product Details
Product Parameters
Packaging and Transportation
Related Products
Leave Us Message
Please give us a message
What are you lookking for?