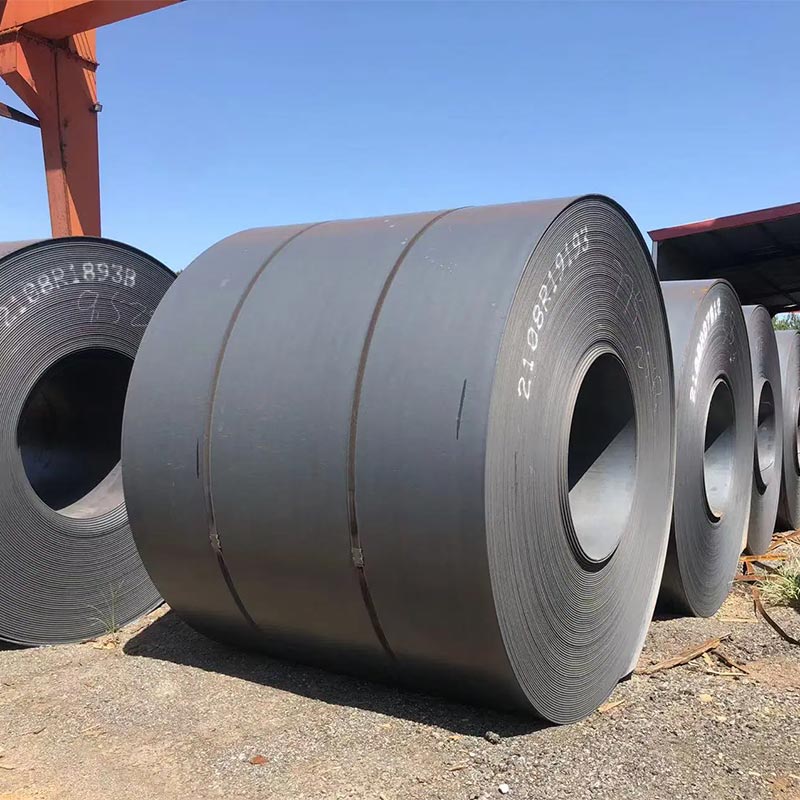
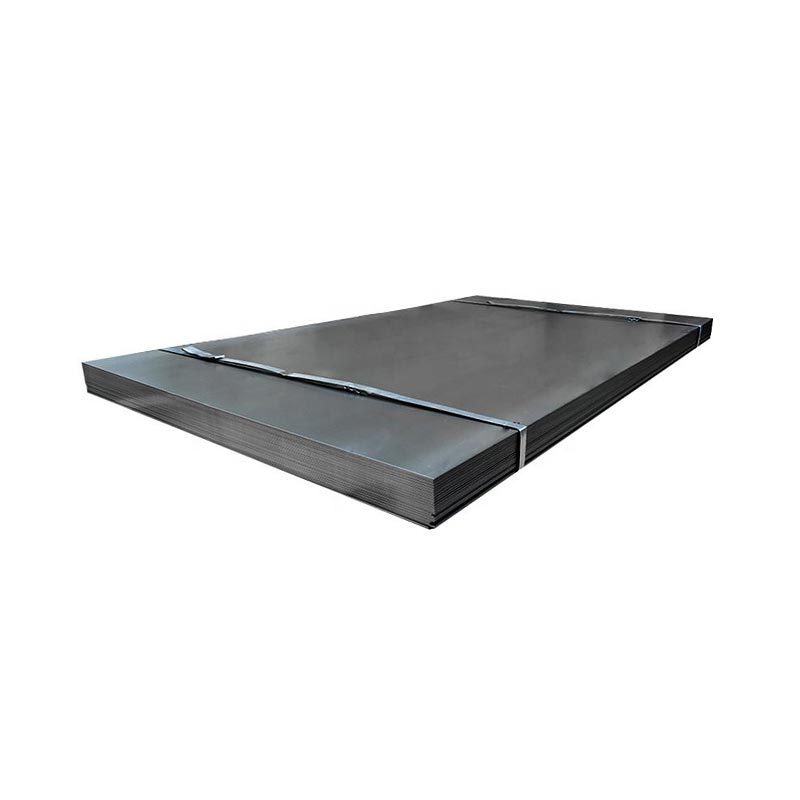
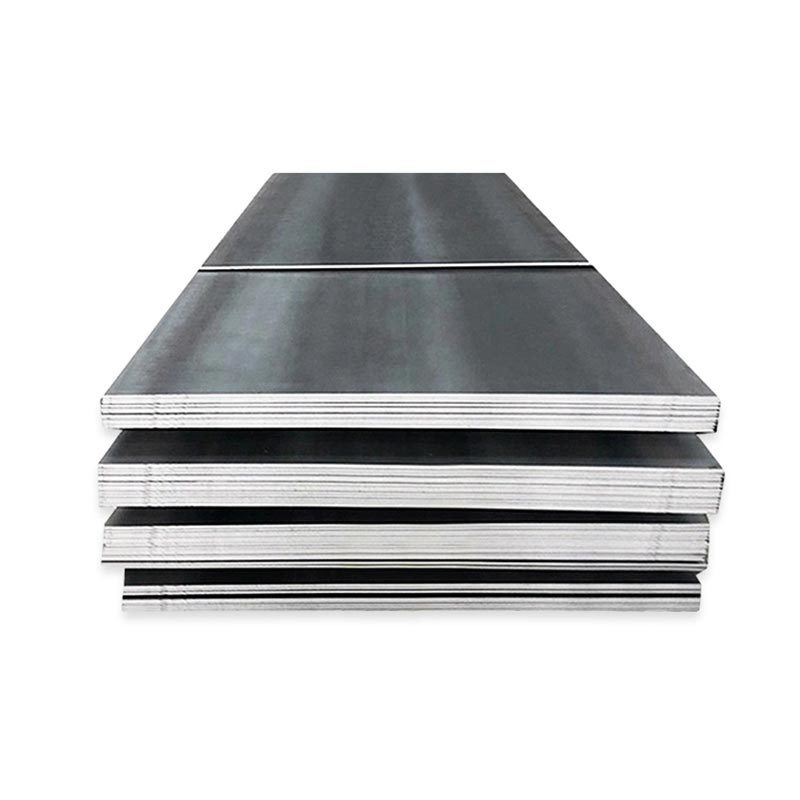
Carbon Steel Coil
● A carbon steel coil is a continuous, rolled sheet of carbon steel (iron-carbon alloy) wound into a coil shape. Classified by carbon content (low, medium, high), it balances formability, strength, and cost.
● Low-carbon coils (e.g., A36) offer ductility and weldability, ideal for automotive parts or construction. Medium-carbon variants provide higher strength, used in machinery. High-carbon types are hard but less flexible, suited for tools.
● Available in various thicknesses and widths, these coils are unrolled for cutting, stamping, or forming. Common in manufacturing, construction, and metalworking, they serve as raw material for pipes, panels, and structural components.
View Video
Mild Steel Coil
Mild steel coil is a low-carbon (≤0.25% C) material, known for its excellent weldability, formability, and machinability. It offers moderate strength (tensile 300–550 MPa) with high ductility, making it easy to bend, cut, or shape. Cost-effective and widely available, it’s used in diverse applications: construction, automotive parts, pipes, containers, and general fabrication. Its versatility and affordability make it a staple in industries needing basic structural or functional components without high-strength requirements.
Get A Quick Quote!
You Can Leave Us A Message
or Send Us An Email!
Product Details
Product Parameters
Packaging and Transportation
Related Products
Leave Us Message
Please give us a message
What are you lookking for?